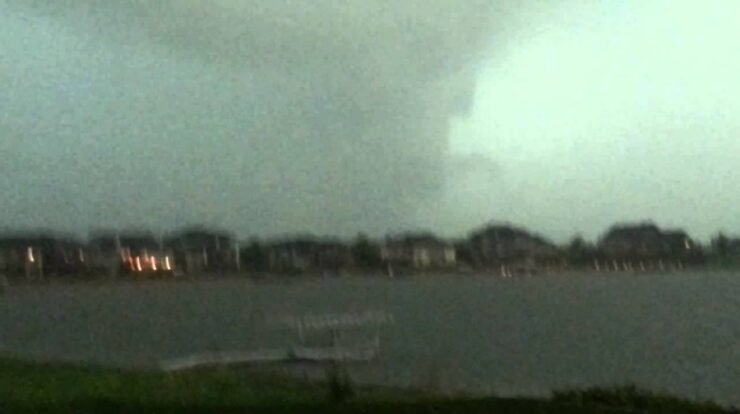
The Elkhorn tornado, a meteorological marvel and a force of nature, has captivated the attention of scientists and communities alike. With its distinct characteristics, devastating impact, and unpredictable nature, the Elkhorn tornado presents a complex challenge that requires a comprehensive understanding for effective preparedness and mitigation.
This article delves into the fascinating world of Elkhorn tornadoes, exploring their unique attributes, the science behind their formation, the challenges of forecasting and warning systems, and the crucial steps individuals and communities can take to prepare for and mitigate their impact.
Tornado Characteristics
Elkhorn tornadoes are a unique type of tornado that exhibits distinct characteristics setting them apart from other tornadoes. These tornadoes are characterized by their:
- Compact size:Elkhorn tornadoes are typically smaller in diameter compared to other tornadoes, often ranging from 50 to 200 yards wide.
- Cone-shaped structure:They have a distinct cone shape, with a narrow base that widens as it rises, resembling an elongated cone.
- High intensity:Despite their smaller size, Elkhorn tornadoes can be extremely intense, often reaching EF3 or higher on the Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF Scale).
Historical records indicate several notable Elkhorn tornadoes, including the devastating 1957 Ruskin Heights tornado in Kansas City, Missouri, which claimed 44 lives and caused extensive damage. Another significant Elkhorn tornado occurred in 1980 in Grand Island, Nebraska, causing widespread destruction and injuries.
The formation of Elkhorn tornadoes is influenced by a combination of atmospheric factors, including:
- Strong updrafts:Powerful updrafts within a thunderstorm can create a rotating column of air, which can develop into an Elkhorn tornado.
- Low-level wind shear:Differences in wind speed and direction at different altitudes can contribute to the formation of the cone shape characteristic of Elkhorn tornadoes.
- Environmental instability:Atmospheric conditions that favor the development of severe thunderstorms, such as high levels of moisture and instability, can increase the likelihood of Elkhorn tornado formation.
Damage Assessment
Assessing the damage caused by Elkhorn tornadoes is crucial for understanding their impact and implementing appropriate recovery measures. Various methods are employed to evaluate the extent of damage:
- Field surveys:Trained damage assessment teams conduct on-site inspections to document the severity of damage to structures, infrastructure, and vegetation.
- Aerial surveys:Helicopters or drones are used to obtain a comprehensive view of the affected area, providing an overview of the damage patterns and identifying areas requiring immediate attention.
- Satellite imagery:Satellite images can provide valuable information about the extent of damage, particularly in remote or inaccessible areas.
The following table Artikels different damage levels and their corresponding characteristics:
| Damage Level | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| EF0 (Weak) | Light damage to trees and vegetation, minor roof damage, broken windows |
| EF1 (Moderate) | Moderate damage to trees and vegetation, significant roof damage, collapse of exterior walls |
| EF2 (Strong) | Severe damage to trees and vegetation, complete roof removal, collapse of exterior and interior walls |
| EF3 (Severe) | Devastating damage to trees and vegetation, complete destruction of structures, collapse of entire buildings |
| EF4 (Devastating) | Extreme damage to trees and vegetation, complete destruction of structures, debris carried long distances |
| EF5 (Catastrophic) | Complete destruction of structures, debris carried extreme distances, ground scouring |
Structures particularly vulnerable to Elkhorn tornado damage include:
- Mobile homes:Due to their lightweight construction and lack of a permanent foundation, mobile homes are highly susceptible to being overturned or destroyed by tornadoes.
- Older buildings:Buildings constructed before modern building codes may not have adequate structural integrity to withstand the forces of a tornado.
- Unreinforced masonry structures:Buildings constructed with unreinforced masonry, such as brick or stone, are vulnerable to collapse during a tornado.
Forecasting and Warning Systems
Forecasting Elkhorn tornadoes is challenging due to their relatively small size and short lifespan. However, meteorologists use various tools and techniques to enhance their ability to predict and warn of these tornadoes:
- Doppler radar:Doppler radar can detect the rotation within thunderstorms and provide valuable information about the likelihood of tornado formation.
- Spotter networks:Trained volunteer spotters observe and report severe weather conditions, including tornadoes, providing ground-level information to supplement radar data.
- Numerical weather prediction models:Computer models can simulate atmospheric conditions and predict the potential for severe weather, including tornadoes.
Current warning systems include:
- Tornado warnings:Issued by the National Weather Service (NWS) when a tornado is imminent or has been spotted, providing critical information to the public.
- Tornado watches:Issued when conditions are favorable for tornado development, advising the public to be prepared and monitor weather conditions.
The effectiveness of tornado warnings depends on factors such as lead time, accuracy, and public response. Successful warnings have resulted in timely evacuations and reduced injuries and fatalities, while unsuccessful warnings can lead to complacency or confusion.
Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
Preparing for and mitigating the impact of Elkhorn tornadoes is essential for public safety and reducing property damage. The following table Artikels steps individuals can take:
| Preparation Steps | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Create an emergency plan | Reinforce roofs and exterior walls |
| Assemble a disaster preparedness kit | Install storm shelters or safe rooms |
| Stay informed about weather forecasts | Trim trees and remove loose objects |
| Identify safe shelter locations | Educate family members about tornado safety |
| Practice tornado drills | Participate in community preparedness programs |
Creating an emergency plan involves identifying evacuation routes, designating a meeting place, and establishing communication methods. A disaster preparedness kit should include essential items such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
Organizations such as the National Weather Service and local emergency management agencies provide resources and guidance for tornado preparedness. These organizations offer educational programs, conduct drills, and distribute materials to help communities prepare for and mitigate the impact of tornadoes.
Ending Remarks

As we continue to unravel the mysteries of Elkhorn tornadoes, scientific research plays a pivotal role in enhancing our understanding, prediction capabilities, and preparedness strategies. By embracing ongoing research and collaboration, we can strive to minimize the devastation caused by these powerful forces of nature and safeguard our communities.
Detailed FAQs: Elkhorn Tornado
What is an Elkhorn tornado?
An Elkhorn tornado is a rare and powerful type of tornado characterized by its large size, cone-shaped appearance, and extreme intensity.
How do Elkhorn tornadoes form?
Elkhorn tornadoes form when strong updrafts within a thunderstorm interact with winds at different speeds and directions, creating a rotating column of air.
What are the challenges of forecasting Elkhorn tornadoes?
Forecasting Elkhorn tornadoes is challenging due to their unpredictable nature and the lack of distinct precursors in weather patterns.